When most people think about geometry and symmetry, they often associate these concepts with mathematics and visual arts. However, there is a fascinating connection between these geometric principles and the world of music. One of the most intriguing examples of this connection can be found in the exploration of Galxe polyhedra.
Galxe polyhedra, also known as “space-filling polyhedra,” are three-dimensional shapes that can completely fill a given space without leaving any gaps. These unique geometrical structures have captivated mathematicians and artists alike, but their presence in the realm of music is less well-known.
Through the lens of musical composition, the symmetries and geometries of Galxe polyhedra provide a rich source of inspiration. Composers have long been interested in exploring mathematical concepts in their music, and the use of Galxe polyhedra opens up new possibilities for creating intricate and harmonious musical patterns.
By mapping the vertices of a Galxe polyhedron onto the notes of a musical scale, composers can create melodies that embody the symmetries and geometries of these fascinating shapes. The resulting compositions often exhibit a mesmerizing sense of order and balance, as well as a deep connection to the underlying mathematical principles.
Exploring the symmetries and geometries of Galxe polyhedra in music not only allows us to appreciate the beauty of these mathematical constructs, but also highlights the fundamental interconnectedness of different artistic disciplines. It is a testament to the power of human creativity and the profound influence that mathematical concepts can have on our artistic expressions.
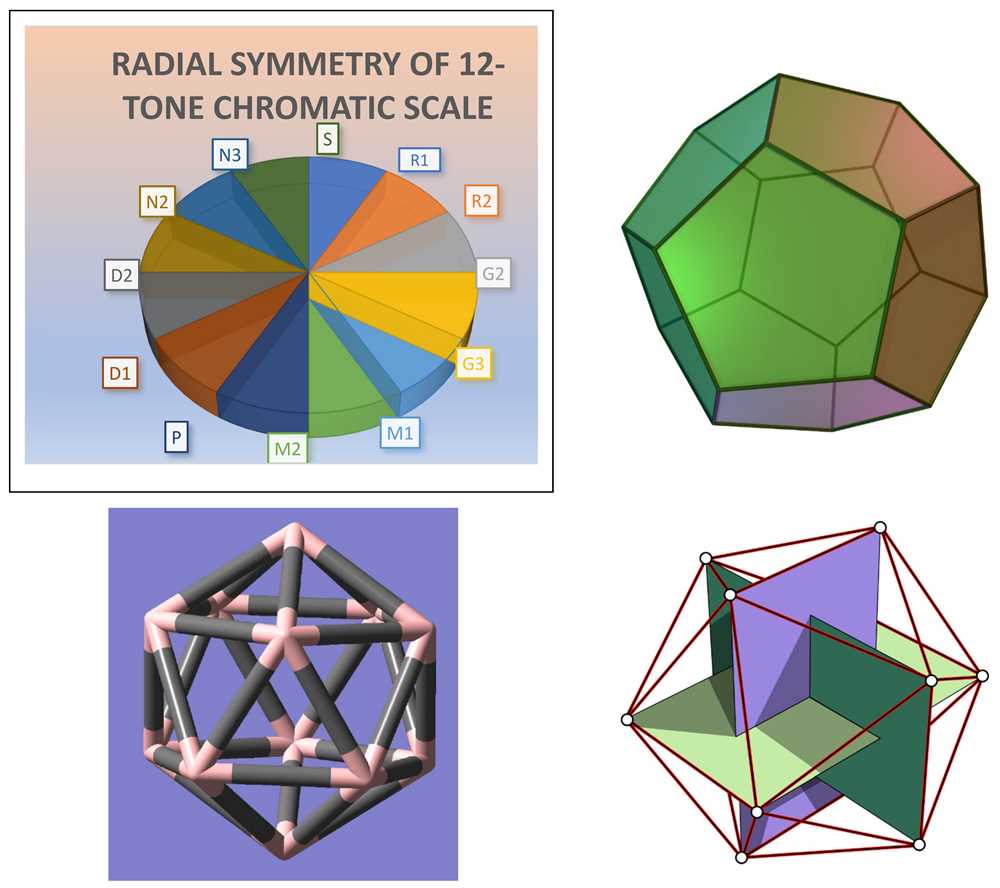
Understanding Galxe polyhedra and their significance in music
Galxe polyhedra are a fascinating mathematical concept that have recently gained attention in the field of music. These intricate three-dimensional structures, also known as Goldberg polyhedra, are named after American mathematician Michael Goldberg who discovered them in the 1990s. They are composed of interconnected polygons, creating a visually stunning and complex geometrical form.
Exploring the symmetries of Galxe polyhedra
One of the key aspects of Galxe polyhedra is their symmetry. These structures exhibit a wide range of symmetries, including rotational, reflectional, and translational symmetries. This makes them a rich source of inspiration for composers and musicians who strive to create harmonious and balanced compositions.
By studying the symmetries of Galxe polyhedra, musicians can gain insight into the relationships between different musical elements such as rhythm, melody, and harmony. The symmetries of these polyhedra can be translated into musical patterns and motifs, allowing composers to create intricate and captivating musical compositions.
The geometrical significance in music
In addition to their symmetrical properties, Galxe polyhedra also have a significant geometrical impact on music. The complex and interconnected polygons that form these polyhedra can be compared to the various melodic and harmonic elements in a musical composition.
By understanding the geometrical properties of Galxe polyhedra, musicians can create unique and innovative musical structures. The interplay between different polygons in these polyhedra can be likened to the interplay between different musical elements, resulting in a dynamic and engaging musical experience.
Furthermore, the geometrical significance of Galxe polyhedra extends beyond the composition itself. They can also serve as a visual representation of the music, allowing listeners to appreciate the underlying structure and complexity of the composition.
Conclusion
Galxe polyhedra offer a fascinating insight into the symmetries and geometries that exist in music. By understanding these structures and their significance, musicians can unlock new possibilities for creating harmonious and captivating compositions. The exploration of Galxe polyhedra in music opens up a world of creativity and innovation, bridging the gap between mathematics and the art of music.
Symmetries of Galxe Polyhedra
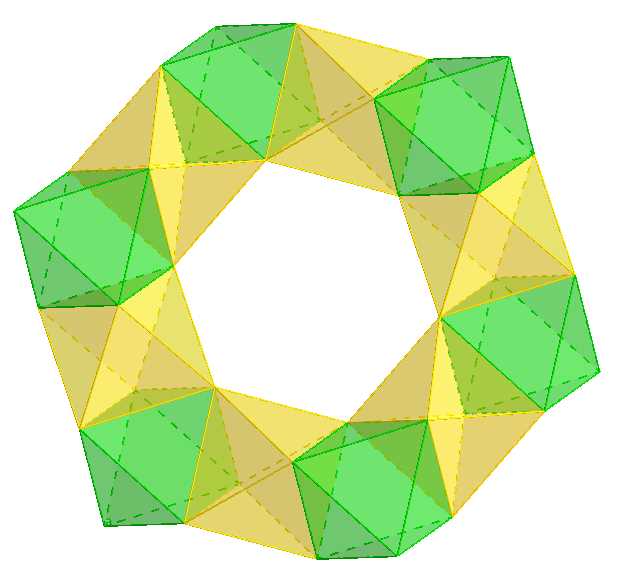
In the realm of geometry, Galxe polyhedra offer a fascinating exploration of symmetries. These polyhedra, named after their discoverer, Professor Galxe, are three-dimensional shapes composed of polygons. What makes Galxe polyhedra unique is their intricate arrangement of polygons, resulting in mesmerizing symmetries.
The symmetries of Galxe polyhedra can be categorized into several types. The first type is reflection symmetry, also known as mirror symmetry. This type of symmetry occurs when a polyhedron can be divided into halves that are mirror images of each other. Imagine holding a mirror along a plane of the polyhedron, and the reflection you see is the other half of the polyhedron.
The second type of symmetry is rotational symmetry. A polyhedron exhibits rotational symmetry when it can be rotated around an axis and still maintain its original appearance. The number of times a polyhedron can be rotated to map onto itself is called its order of symmetry. Some Galxe polyhedra have a high order of rotational symmetry, making them especially intriguing.
Another type of symmetry found in Galxe polyhedra is translational symmetry. This symmetry occurs when a polyhedron can be shifted along a straight line without changing its overall appearance. Think of it as sliding the polyhedron without rotating or reflecting it. Translational symmetry adds a sense of fluidity and continuity to the structure of Galxe polyhedra.
Lastly, Galxe polyhedra can also exhibit a combination of these symmetries, resulting in a unique interplay of reflections, rotations, and translations. In some cases, these combinations can create mesmerizing patterns and visual effects.
Studying the symmetries of Galxe polyhedra can have applications beyond geometry. For instance, composers and musicians have experimented with translating these symmetries into music, creating intricate compositions that mirror the symmetrical beauty of Galxe polyhedra. Exploring the symmetries and geometries of Galxe polyhedra in music opens up a whole new realm of artistic expression.
- The reflection symmetry of Galxe polyhedra adds depth and balance to musical compositions.
- The rotational symmetry of Galxe polyhedra can be translated into rhythmic patterns and motifs.
- The translational symmetry of Galxe polyhedra can be represented by melodic phrases that seamlessly flow together.
- The interplay of these symmetries creates a harmonious and captivating musical experience.
In conclusion, the symmetries of Galxe polyhedra offer a rich and captivating avenue for exploration. From their reflection and rotational symmetries to their translational symmetry, these polyhedra provide endless possibilities for artistic expression in various fields, including music. By delving into the symmetries and geometries of Galxe polyhedra, we can unlock new realms of creativity and appreciation for the beauty of mathematics and the arts.
Exploring the various symmetries exhibited by Galxe polyhedra
Galxe polyhedra are fascinating geometric shapes that exhibit a wide range of symmetries. These symmetries can be studied and explored in the context of music, creating a unique and captivating musical experience.
Symmetry in Galxe polyhedra

Galxe polyhedra possess symmetries that can be categorized into several types:
- Rotational symmetries: Galxe polyhedra can have rotational symmetries of various degrees. This means that the polyhedra can be rotated by a certain angle and still look the same.
- Reflection symmetries: Some Galxe polyhedra have reflection symmetries, meaning that they can be reflected across a plane and still retain their overall shape.
- Translational symmetries: Certain Galxe polyhedra exhibit translational symmetries, which means that they can be translated or shifted in space and maintain their form.
- Inversion symmetries: Galxe polyhedra can also possess inversion symmetries, where the polyhedra can be inverted or turned inside out and still maintain their symmetry.
Musical exploration of symmetries

The symmetries exhibited by Galxe polyhedra provide an interesting basis for exploring and creating music. By mapping the symmetries onto musical structures, composers and musicians can create unique compositions that reflect the inherent beauty and harmony found in these geometric shapes.
One approach to exploring these symmetries in music is to assign different musical elements to each type of symmetry. For example, rotational symmetries can be represented by repeating musical patterns or motifs, while reflection symmetries can be expressed through mirror-like musical phrases.
Musicians can also experiment with different musical scales, rhythms, and harmonies inspired by the symmetries of Galxe polyhedra. These musical elements can be manipulated and transformed based on the different types of symmetries, resulting in a rich and diverse musical composition.
| Type of Symmetry | Description |
|---|---|
| Rotational Symmetry | This symmetry involves rotating the Galxe polyhedra by a certain angle and maintaining its appearance. |
| Reflection Symmetry | This symmetry involves reflecting the Galxe polyhedra across a plane and retaining its overall shape. |
| Translational Symmetry | This symmetry involves shifting or translating the Galxe polyhedra in space while preserving its form. |
| Inversion Symmetry | This symmetry involves inverting or turning the Galxe polyhedra inside out and maintaining its symmetry. |
By exploring the various symmetries exhibited by Galxe polyhedra in music, composers and musicians can create unique and enchanting compositions that blend the beauty of geometric shapes with the artistry of sound.
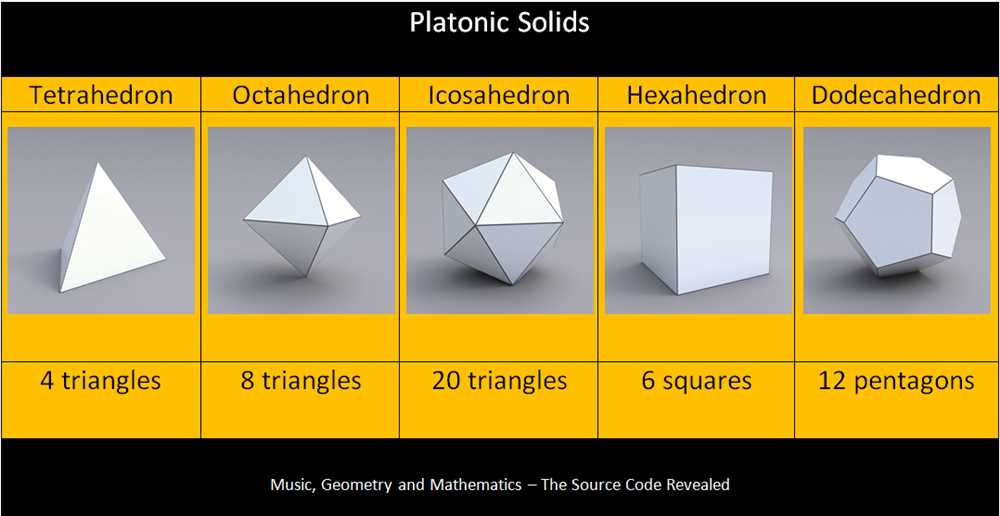
Geometries of Galxe Polyhedra
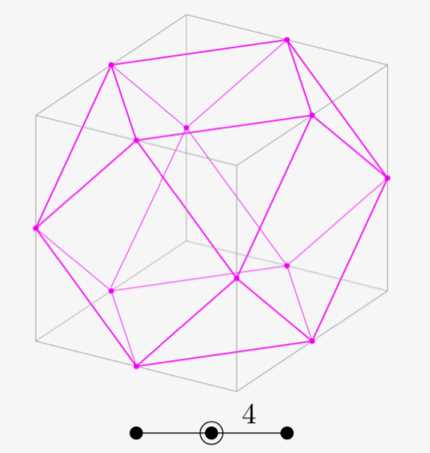
Galxe polyhedra are a fascinating class of geometric structures that exhibit a wide variety of symmetries and shapes. They are formed by combining multiple identical regular polygons to form three-dimensional structures.
The uniqueness of Galxe polyhedra lies in their ability to showcase the symmetries and geometries inherent in the underlying regular polygons. The different ways in which the polygons can be arranged and connected result in a rich assortment of polyhedral shapes.
One of the key properties of Galxe polyhedra is their symmetry. They often possess multiple axes of symmetry, which allows for rotations and reflections that preserve the overall shape. These symmetries can be visualized by examining the arrangement of the polygons and the angles between them.
The geometries of Galxe polyhedra can vary greatly depending on the types and number of polygons used. They can range from simple prisms and pyramids formed by connecting regular polygons to more complex structures such as dodecahedra and icosahedra.
Furthermore, Galxe polyhedra can also exhibit interesting properties such as planarity, where all polygon faces lie on a single plane, or non-planarity, where the faces are twisted and folded in three-dimensional space.
In conclusion, the geometries of Galxe polyhedra offer a fascinating exploration of the symmetries and shapes inherent in regular polygons. Their intricate structures and diverse properties provide a rich field for study and artistic expression.
Analyzing the intricate geometries of Galxe polyhedra and their relation to music

Galxe polyhedra are fascinating geometric structures that have been a subject of exploration and analysis for centuries. These polyhedra, also known as stellation polyhedra, are formed by extending the faces of a given base polyhedron until they meet to form new vertices and edges, creating intricate and symmetrical patterns.
One of the most interesting aspects of Galxe polyhedra is their connection to music. Music, like geometry, is based on patterns and symmetries. The harmonies and melodies that we hear in music can be seen as patterns of sound frequencies and durations. Similarly, the symmetrical structures of Galxe polyhedra can be thought of as patterns of vertices, edges, and faces.
By studying the geometrical properties of Galxe polyhedra, we can gain insights into the mathematical relationships that underlie musical compositions. For example, we can analyze the symmetrical arrangements of vertices and edges in a Galxe polyhedron and relate them to the harmonic structures of a musical piece. We can also explore the regularity and repetition in the polyhedra’s faces and connect them to the rhythmic patterns in music.
This analysis can be done using tools from mathematics and music theory. By applying concepts such as symmetry groups, tessellations, and rhythm patterns, we can create mathematical models of Galxe polyhedra and use them to generate musical compositions. This allows us to explore the deep connections between geometry and music and to create unique and intriguing musical pieces.
In conclusion, analyzing the intricate geometries of Galxe polyhedra can provide us with a deeper understanding of the mathematical and aesthetic principles that underlie music. By exploring the symmetries and patterns in these polyhedra, we can unlock new possibilities for composition and create music that reflects the beauty and complexity of the geometrical world.
Application in Music

Exploring the symmetries and geometries of Galxe polyhedra has great potential in the field of music. These polyhedra possess intricate and mesmerizing symmetrical patterns that can be translated into musical compositions.
One way to utilize Galxe polyhedra in music is by assigning musical notes to different facets or vertices of the polyhedra. This can create a unique melody or harmony that is based on the geometric structure of the polyhedron.
Furthermore, the symmetries of Galxe polyhedra can inspire rhythmic patterns in music. By analyzing the orientation and arrangement of the polyhedra’s faces, musicians can create complex and interesting rhythms that reflect the symmetrical properties of the polyhedra.
Additionally, Galxe polyhedra can be used as visual aids during live performances. The intricate and visually stunning nature of these polyhedra can enhance the overall visual experience for the audience.
Overall, incorporating the symmetries and geometries of Galxe polyhedra into music opens up a new realm of creative possibilities. It allows composers and musicians to explore unique musical structures and patterns that are inspired by the beauty of geometry.
Question-answer:
How are Galxe polyhedra related to music?
Galxe polyhedra are related to music through a process called sonification. Sonification is the conversion of data or other abstract concepts into sound, and in this case, Galxe polyhedra are used to create musical compositions. The symmetries and geometries of Galxe polyhedra provide a structure for creating unique and interesting musical patterns.
Can you explain more about the symmetries and geometries of Galxe polyhedra?
Galxe polyhedra exhibit various symmetries and geometrical properties. They have rotational symmetries, which means that they can be rotated by certain angles and still look the same. They also have reflective symmetries, where they can be mirrored along certain lines and still retain their original shape. In terms of geometries, Galxe polyhedra have different types of faces, edges, and vertices, which contribute to their overall structure and aesthetic appeal.
How are Galxe polyhedra compositions created?
Galxe polyhedra compositions are created by assigning musical parameters to the symmetries and geometries of the polyhedra. For example, different rotations of the polyhedra can correspond to different musical intervals or rhythms, while mirror reflections can be represented by changes in dynamics or timbre. By mapping these musical parameters to the symmetries and geometries, composers are able to create unique and expressive musical compositions.


