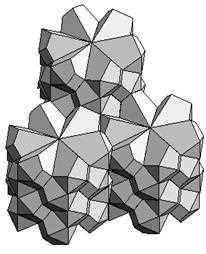
The exploration of space-filling polyhedra has been a fascinating topic in mathematics for many years. These unique structures have the remarkable ability to fill three-dimensional space without leaving any gaps, and their mathematical properties have intrigued mathematicians and scientists alike.
Galxe polyhedra are a specific class of space-filling polyhedra that have gained significant attention due to their complex and intricate geometrical properties. The name “Galxe” is derived from the combination of “Galaxy” and “Polyhedra,” emphasizing the vastness and richness of their structure.
One of the most intriguing aspects of Galxe polyhedra is their ability to form highly symmetric patterns. These patterns exhibit various symmetries, including rotational, reflectional, and even self-similarity. The symmetries of these polyhedra make them aesthetically pleasing and inspire further mathematical investigations.
The mathematical study of Galxe polyhedra involves exploring their topological properties, such as connectivity and compactness, as well as their geometric properties, such as surface area and volume. These properties provide valuable insights into the behavior and characteristics of these complex structures.
Furthermore, Galxe polyhedra have also found applications in diverse fields, including materials science, architecture, and computer graphics. Their unique properties make them suitable for designing efficient and robust structures, as well as generating visually appealing patterns and textures.
In this article, we will delve into the mathematical properties of space-filling Galxe polyhedra, exploring their symmetries, topological and geometric properties, as well as their applications in various fields. By gaining a deeper understanding of these fascinating structures, we can unlock new possibilities and applications in mathematics and beyond.
Overview of Space-Filling Galxe Polyhedra
Space-filling Galxe polyhedra are fascinating mathematical objects that have captured the attention of researchers. These polyhedra are three-dimensional structures that can fill a space without leaving any gaps.
Definition
A space-filling Galxe polyhedron is a polyhedral representation of a Galxe crystal structure, which is a theoretical arrangement of atoms or molecules in three-dimensional space. These polyhedra are constructed by connecting the vertices of a regular polyhedron with additional edges, resulting in a complex and interconnected network.
Properties
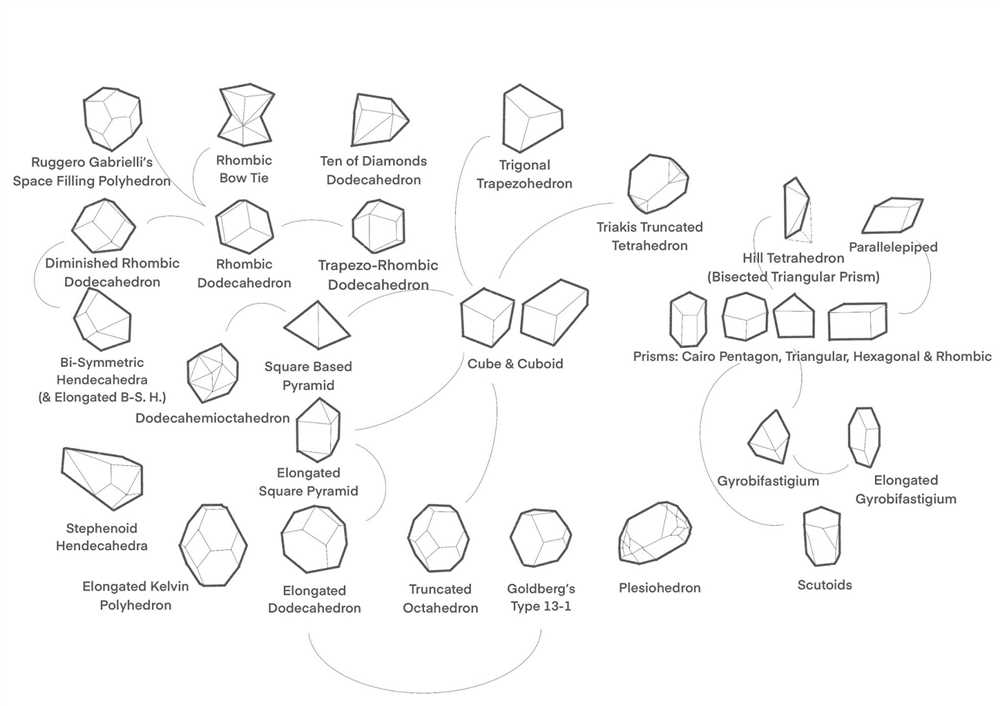
Space-filling Galxe polyhedra exhibit several interesting mathematical properties. They have a high degree of symmetry and can be classified into different types based on their connectivity and arrangement of vertices. These polyhedra also have a well-defined volume and surface area, which can be calculated using mathematical formulas.
Furthermore, space-filling Galxe polyhedra have been found to possess unique topological properties. They can form intricate networks with tunnels, voids, and cavities of various sizes and shapes. These properties make them suitable for applications in materials science, such as designing porous materials with specific properties or modeling the behavior of complex fluids.
Applications
The study of space-filling Galxe polyhedra has applications in various fields, including crystallography, chemistry, and physics. These polyhedra can be used to model and analyze the atomic or molecular arrangement in crystals, study the behavior of complex materials, and understand the properties of amorphous solids.
In addition, space-filling Galxe polyhedra have practical applications in the design of porous materials for adsorption, separation, and catalysis. By manipulating the structure of these polyhedra, researchers can create materials with tailored properties, such as high surface area, selective adsorption, or enhanced catalytic activity.
Overall, the study of space-filling Galxe polyhedra provides valuable insights into the mathematical properties of three-dimensional structures and their applications in various scientific disciplines. It continues to be an active area of research, with new discoveries and applications emerging regularly.
Mathematical Properties

Space-filling polyhedra are fascinating mathematical objects that have been extensively studied for their unique geometric and topological properties. Here, we explore some of the key mathematical properties of these polyhedra:
Euler’s Formula
Euler’s formula is a fundamental theorem in polyhedral geometry that relates the number of vertices (V), edges (E), and faces (F) of a polyhedron. For space-filling Galxe polyhedra, Euler’s formula can be stated as:
V – E + F = 2
Packing Efficiency
Packing efficiency is another important property of space-filling polyhedra. It measures how efficiently space is utilized by the polyhedron. The packing efficiency of a Galxe polyhedron is defined as the ratio of the volume occupied by the polyhedron to the total volume of the space it fills. Achieving high packing efficiency is a desirable property in many applications, such as materials science and packing problems.
These mathematical properties play a crucial role in the understanding and analysis of space-filling Galxe polyhedra. Further investigation of these properties can lead to insights into their unique geometric and topological characteristics, as well as potential applications in various fields.
Applications and Implications
The study of mathematical properties of space-filling Galxe polyhedra holds several applications and implications in various fields. Some of the key areas where these findings can have an impact include:
Architecture and Design
Understanding the properties of space-filling Galxe polyhedra can inspire new architectural designs and structures. These polyhedra can be used as the basis for innovative building shapes that maximize space utilization and create unique visual experiences. Architects and designers can explore the possibilities of incorporating these polyhedra into their projects to create visually striking and functional spaces.
Engineering and Manufacturing
The mathematical properties of space-filling Galxe polyhedra can have implications in the fields of engineering and manufacturing. By studying these polyhedra, engineers can develop new approaches to optimize the use of materials and minimize waste in building processes. In manufacturing, these findings can provide insights into efficient packing and transportation of goods, leading to cost savings and environmental benefits.
Mathematics and Geometry
The study of space-filling Galxe polyhedra contributes to the field of mathematics and geometry. Researchers can explore the mathematical properties of these polyhedra to deepen our understanding of geometric principles and expand the existing knowledge base. These findings can also lead to the development of new mathematical models and techniques for solving complex problems in various disciplines.
- Art and Sculpture: Artists can draw inspiration from the intricate forms of space-filling Galxe polyhedra and incorporate them into their sculptures and artworks.
- Computer Graphics and Animation: The mathematical properties of these polyhedra can be utilized in computer graphics and animation to create visually captivating 3D models and environments.
- Chemistry and Material Science: The study of space-filling Galxe polyhedra can provide insights into the structure and behavior of molecules and materials, leading to advancements in fields such as chemistry and material science.
In conclusion, the exploration of mathematical properties of space-filling Galxe polyhedra has diverse applications and implications across various fields, including architecture, engineering, mathematics, art, computer graphics, and chemistry. These findings can inspire new designs and structures, optimize manufacturing processes, contribute to mathematical and geometric knowledge, and advance other scientific disciplines.
Question-answer:
What are space-filling polyhedra?
Space-filling polyhedra are three-dimensional figures that can completely fill a given space without leaving any gaps.
What are some examples of space-filling polyhedra?
Some examples of space-filling polyhedra include the rhombic dodecahedron, the truncated octahedron, and the hexagonal prism.


