
The universe, with its infinite expanse and wonder, has always captured the imagination of humanity. We have gazed up at the night sky, marveling at the celestial bodies that twinkle above us. For centuries, astronomers have sought to understand the mysteries of the universe, and one of their greatest endeavors has been the exploration of galaxies.
Galaxies, those cosmic islands of stars, gas, and dust, are the building blocks of the universe. They come in various shapes and sizes, ranging from small dwarf galaxies to massive elliptical galaxies. But have you ever wondered just how many galaxies exist in the vast expanse of space? Prepare to be amazed – there are an estimated 65,357 known galaxies in the observable universe.
Embarking on a journey through the vast universe, we will encounter a stunning array of galaxies. Our first stop takes us to the Milky Way, our home galaxy. Spanning approximately 100,000 light-years in diameter, the Milky Way is a spiral galaxy with a distinctive bar at its center. It is home to billions of stars, including our very own Sun.
As we venture further into the cosmos, we encounter spiral galaxies with their elegant, swirling arms. These galaxies, like the Andromeda Galaxy and the Whirlpool Galaxy, captivate us with their beauty and grace. We also come across elliptical galaxies, which are older and more massive, filled with ancient stars that have journeyed through the eons.
But the universe holds even more surprises for us. We discover irregular galaxies, such as the Small Magellanic Cloud, which have no defined shape but are teeming with young stars and gas clouds. And let’s not forget about the majestic cosmic collisions, where galaxies collide and merge, creating breathtaking displays of cosmic fireworks.
So join us on this extraordinary journey as we explore the 65,357 galaxies that populate our vast universe. From the smallest dwarf galaxy to the grandest spiral, each galaxy holds its own unique story and offers a glimpse into the immense beauty and complexity of our cosmic home.
Discovering the Mysteries Beyond Earth
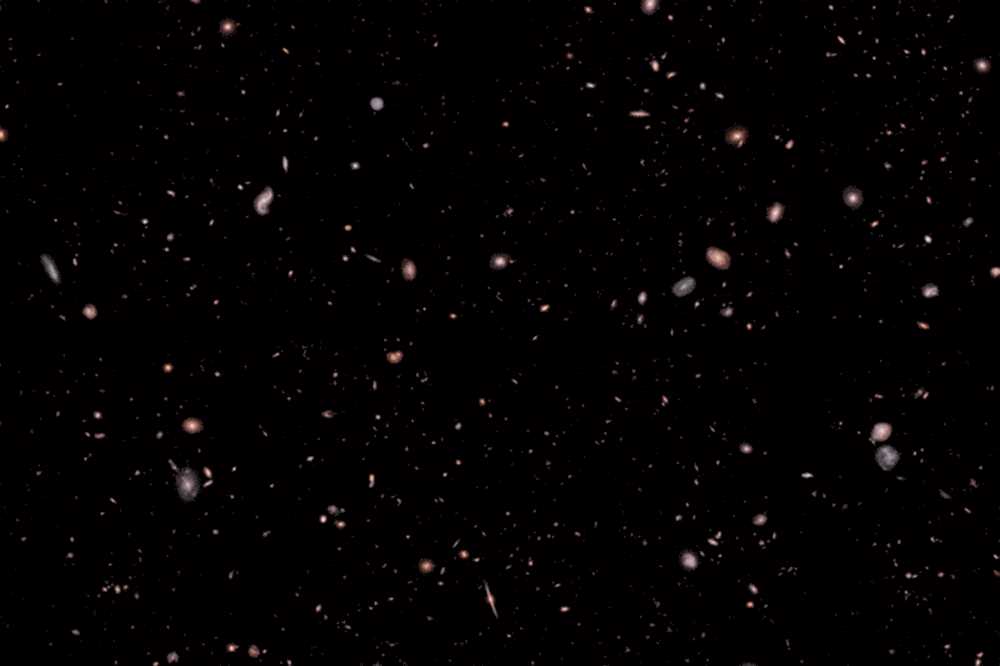

The exploration of space has always captured the imagination of mankind. From the early days of gazing up at the stars, to the incredible technological advancements of today, humans have been driven by a desire to understand what lies beyond Earth.
One of the primary goals of space exploration is to discover whether there is life beyond our planet. Scientists have sent countless missions to Mars and other celestial bodies in search of evidence of microbial life or even signs of habitable conditions. While the search has not yet yielded definitive results, the discovery of water on other planets and moons has sparked hope that life may indeed exist beyond Earth.
In addition to the search for life, space exploration also aims to unravel other mysteries of the universe. The study of galaxies, black holes, and other cosmic phenomena provides invaluable insights into the nature of the universe and our place in it. Scientists use powerful telescopes and advanced technology to observe distant galaxies and gather data about their composition, movement, and behavior.
Another intriguing aspect of space exploration is the potential for discovering new resources. With Earth’s finite resources being depleted at an alarming rate, the exploration of asteroids and other celestial bodies for valuable minerals and metals becomes increasingly important. Asteroids, for example, are rich in precious metals such as platinum and gold, making them potentially lucrative sources for future mining expeditions.
Space exploration also has profound implications for technology and innovation. Many of the advancements made in materials science, communications, and robotics can be traced back to space-related research and development. The quest to explore the universe pushes the boundaries of human knowledge and drives the creation of new technologies that have far-reaching applications on Earth.
In conclusion, the exploration of space holds great promise for unraveling the mysteries of the universe and expanding our understanding of the cosmos. Whether it is the search for life, the study of galaxies, or the quest for valuable resources, space exploration pushes the boundaries of human achievement and inspires us to dream of what lies beyond Earth.
Galaxy Formation and Evolution
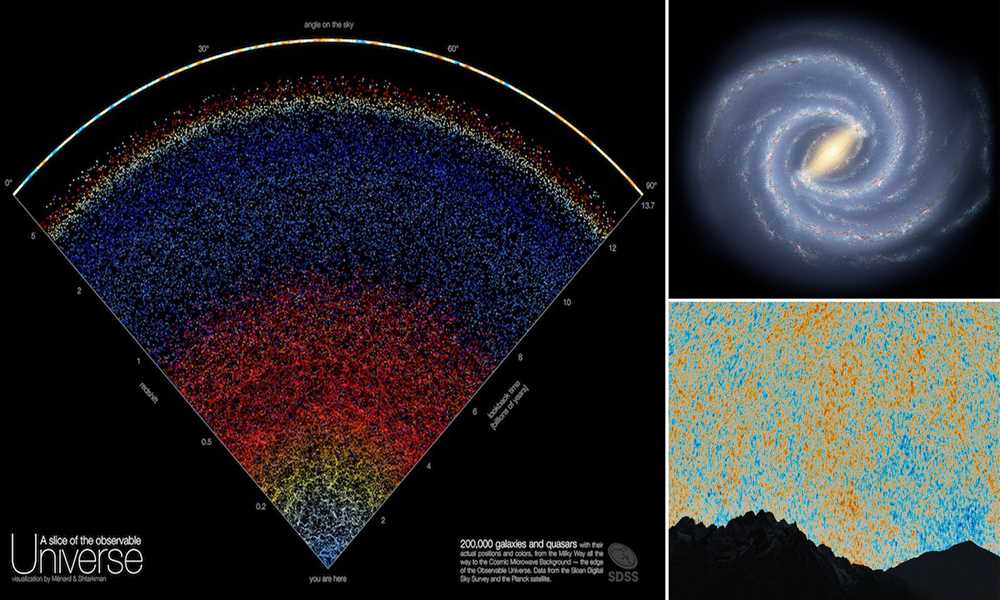
The formation and evolution of galaxies is a complex and fascinating process that has puzzled astronomers for centuries. Galaxies are vast systems of stars, gas, and dark matter that form the building blocks of the universe. Understanding how galaxies form and evolve is crucial to our understanding of the universe as a whole.
Galaxies are believed to have formed from the gravitational collapse of regions of gas and dust in the early universe. Over billions of years, these collapsed regions grew in size and complexity, eventually forming the galaxies we observe today. The exact details of this process are still not fully understood, but current theories suggest that small density fluctuations in the early universe played a crucial role in the formation of galaxies.
As galaxies formed, they underwent a process of evolution, driven by various factors such as mergers, interactions with other galaxies, and the consumption of gas and dust to form new stars. These processes can lead to the creation of new stars, the growth of supermassive black holes at the centers of galaxies, and the redistribution of matter within the galaxy.
Galaxy Mergers
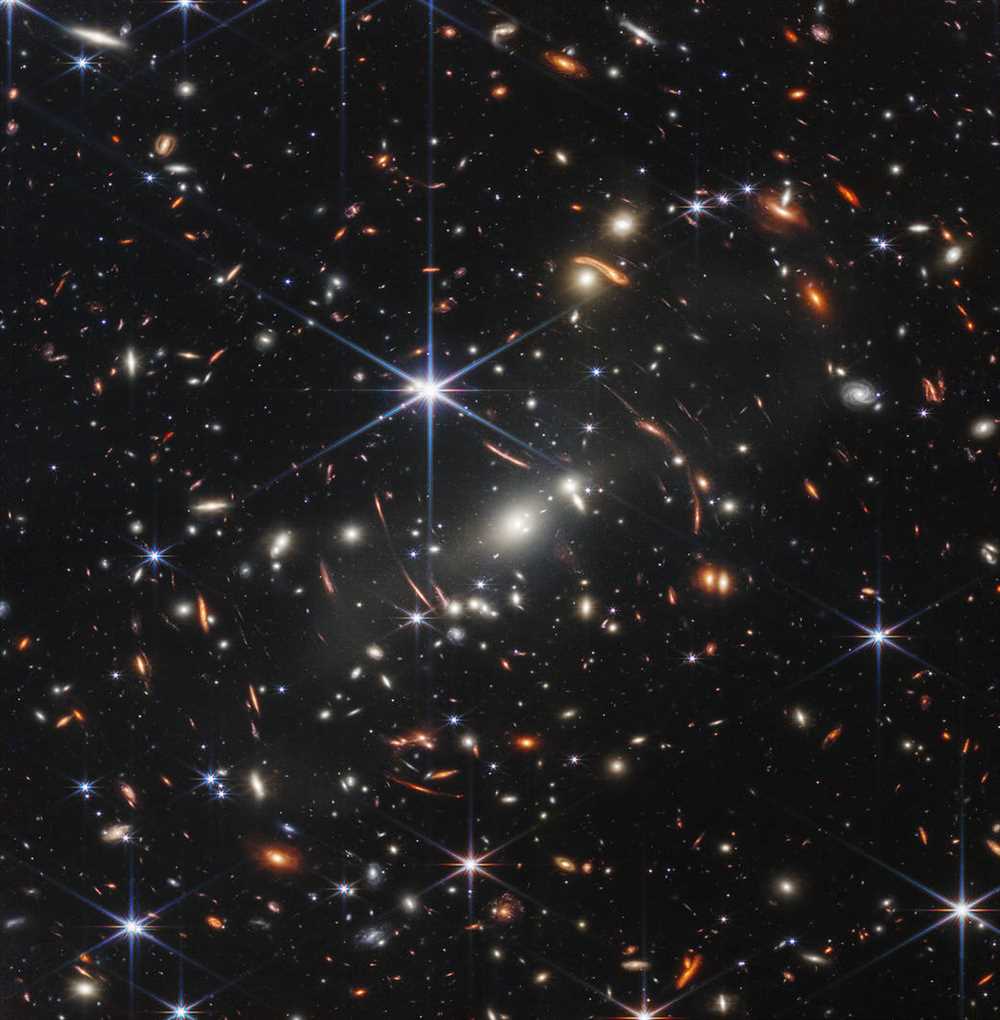

Galaxy mergers occur when two or more galaxies collide and join together to form a new, larger galaxy. These mergers can result in significant changes to the structure and properties of the galaxies involved. For example, a merger can trigger a burst of star formation as gas and dust from the colliding galaxies are compressed and collapse to form new stars.
Galaxy mergers can also lead to the formation of elliptical galaxies, which are characterized by their smooth, featureless appearance. Elliptical galaxies are thought to be the result of major mergers between two or more spiral galaxies, which strips away the gas and dust and disrupts the spiral structure.
Active Galactic Nuclei

At the centers of many galaxies, including our own Milky Way, there are supermassive black holes. These black holes can become active, emitting vast amounts of energy and radiation. These active galactic nuclei (AGN) can have a profound effect on the evolution of galaxies.
AGN can release intense jets of high-energy particles, which can interact with the surrounding gas and dust in the galaxy. This interaction can heat up the gas, suppress star formation, and influence the distribution of matter within the galaxy. AGN activity is believed to be triggered by the accretion of matter onto the black hole, either through mergers with other galaxies or through the gradual infall of gas and dust.
Unraveling the Birth and Life of Galaxies

Galaxies, those magnificent cosmic structures, have always fascinated astronomers and scientists throughout history. These colossal conglomerations of stars, gas, and dust hold the secrets of the universe’s history, as they have witnessed its evolution from its very beginning. Understanding how galaxies are born and how they evolve over time has been a key focus of research in the field of astrophysics.
The birth of a galaxy is a spectacular cosmic event that occurs when immense clouds of gas and dust collapse under their own gravity. As these clouds collapse, they begin to spin, forming a disk-like structure known as a protoplanetary disk. Within this disk, the gravitational forces continue to pull in more and more matter, causing it to heat up and form dense regions called protostars.
Over time, these protostars gather more gas and dust, growing in mass and eventually reaching a critical point where nuclear fusion ignites within their cores. At this point, a star is born, emitting intense radiation and stellar winds that clear away the remaining gas and dust from the protoplanetary disk.
Meanwhile, within the disk, some of the remaining gas and dust begins to clump together due to gravitational forces. These clumps, known as planetesimals, collide and merge, forming larger bodies called protoplanets. The protoplanets continue to grow by accreting more material, eventually becoming fully formed planets.
As the protostars and planets continue to mature, their surroundings begin to shape the structure of the galaxy. Stellar winds, supernovae, and other energetic phenomena start to blow away the remaining gas and dust, clearing the path for the development of star clusters and nebulae.
Throughout their lives, galaxies continue to evolve and change. They interact with neighboring galaxies, merging and colliding, changing their shapes and structures. These interactions can give rise to the formation of new stars, trigger bursts of intense star formation, and even lead to the creation of supermassive black holes at their cores.
Studying the birth and life of galaxies is not only a fascinating scientific endeavor but also crucial for understanding the origins and dynamics of our universe. By unraveling their mysteries, scientists can gain insights into the fundamental laws of physics, the formation of elements, and the processes that shape the cosmos as we know it.
The Diversity of Galaxies

The vast universe is home to an incredible array of galaxies, each with its own unique characteristics and features. From spiral galaxies to elliptical galaxies, the diversity of galactic formations is truly awe-inspiring.
One of the most common types of galaxies is the spiral galaxy. These galaxies are easily recognizable by their swirling arms, which are filled with countless stars, gas, and dust. The spiral arms give these galaxies a mesmerizing appearance, resembling a pinwheel spinning through space. Some spiral galaxies, like the Andromeda Galaxy, are so large that they can contain billions of stars.
On the other hand, elliptical galaxies have a more oval or spherical shape. Unlike spiral galaxies, they lack the distinctive arms and tend to have older stars. These galaxies can range in size from small and compact to massive giants that dwarf their spiral counterparts. Elliptical galaxies are believed to form through the collisions and mergers of other galaxies, resulting in their unique shapes and structures.
In addition to spiral and elliptical galaxies, there are also irregular galaxies. These galaxies do not have a defined shape or structure and often appear chaotic. Irregular galaxies can be smaller and more compact, or they can be larger and contain regions of intense star formation. The irregular shape of these galaxies is often a result of gravitational interactions with other nearby galaxies.
Furthermore, galaxies can be categorized based on their color. Blue galaxies tend to have a higher rate of star formation, while red galaxies are often older and contain more evolved stars. The color of a galaxy can provide valuable insights into its age and evolutionary history.
Studying the diversity of galaxies allows scientists to gain a deeper understanding of the universe’s evolution and the forces that shape it. By examining the size, shape, and composition of these celestial objects, astronomers can piece together the puzzle of how galaxies form, evolve, and interact with one another.
As our exploration of the universe continues, we are bound to discover even more fascinating and unique galaxies. Each new finding brings us closer to unraveling the mysteries of the cosmos and appreciating the incredible diversity that exists beyond our own planet.
Exploring the Different Types of Galaxies
As we journey through the vast universe, we encounter a wide variety of galaxies. These galaxies come in different shapes, sizes, and formations, each with its own unique characteristics. Let’s take a closer look at some of the different types of galaxies we can explore:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Spiral Galaxies | Spiral galaxies are characterized by their distinct spiral arms, which contain a mix of older and younger stars. They often have a central bulge and a rotating disk. |
| Elliptical Galaxies | Elliptical galaxies have an ellipsoidal shape and lack the spiral arms seen in spiral galaxies. They are typically made up of older stars and have little ongoing star formation. |
| Irregular Galaxies | Irregular galaxies are galaxies that do not have a defined shape or structure. They can range from small and compact to larger and more chaotic. They often contain young stars and gas clouds. |
| Lenticular Galaxies | Lenticular galaxies are a hybrid between spiral and elliptical galaxies. They have a disk-like shape similar to spiral galaxies but lack the pronounced spiral arms. |
| Dwarf Galaxies | Dwarf galaxies are small galaxies that contain fewer stars and less mass compared to larger galaxies. They can be found in a variety of shapes, including irregular and elliptical. |
By studying the different types of galaxies, scientists can learn more about the formation and evolution of our universe. Each type offers valuable insights into the processes that shape galaxies and the wider cosmos.
So, the next time you gaze up at the night sky, remember that there is a vast array of galaxies out there, just waiting to be explored and understood.
Exploration and Observation Techniques

Exploring the vast universe and observing the countless galaxies require advanced techniques and technology. Here are some of the exploration and observation techniques used by scientists:
Telescopes: Telescopes are essential tools for exploring the galaxies. They can detect and capture light from distant celestial objects, allowing scientists to analyze and study their properties. Through telescopes, astronomers can observe the position, motion, and composition of galaxies.
Radio Astronomy: Radio telescopes are used to observe galaxies by capturing radio waves emitted by celestial objects. By analyzing the radio signals, scientists can gather information about the structure, kinematics, and magnetic fields of galaxies. This technique helps in studying galaxies that may not be visible in optical light.
Spectroscopy: Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction between light and matter. It allows scientists to analyze the electromagnetic spectrum emitted by galaxies. By using spectrographs, scientists can determine the chemical composition and temperature of galaxies, as well as their motion and distance from Earth.
Hubble Space Telescope: The Hubble Space Telescope, launched by NASA in 1990, revolutionized our understanding of galaxies. It captures high-resolution images and collects data from deep space, allowing scientists to study distant galaxies and their evolution over time.
Gravitational Lensing: Gravitational lensing is a phenomenon that occurs when the light from a distant galaxy is bent and magnified by the gravitational force of a massive object, such as a galaxy cluster. This technique helps scientists study the distribution of dark matter in galaxies and map their gravitational potentials.
Computer Simulations: Computer simulations play a crucial role in understanding the formation and evolution of galaxies. By using complex algorithms, scientists can recreate the conditions of the early universe and simulate the processes that give rise to galaxies. These simulations help validate observations and test different theories about galaxy formation.
With these exploration and observation techniques, scientists can unravel the mysteries of the universe one galaxy at a time. The knowledge gained from studying galaxies helps us better understand the origins of the universe and our place within it.
Question-answer:
How many galaxies are there in the universe?
There are approximately 65,357 galaxies in the universe.
What is the significance of exploring galaxies?
Exploring galaxies is significant because it helps us understand the vastness of the universe and gain insights into its origins and evolution.
Is it possible for humans to visit these galaxies?
Currently, human space travel is limited to our own solar system. Visiting galaxies outside of our own is currently not feasible due to the enormous distances involved.


